Eco-Friendly Heating: How Wood Stoves Benefit the Environment
David Murray
In today’s climate-conscious world, there’s an ever-growing emphasis on sustainable living. From the food we consume to the vehicles we drive, every aspect of our daily lives is being reevaluated in the context of its environmental impact. Central to this conversation is the way we heat our homes. Traditional heating methods, reliant on fossil fuels, have long been identified as significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions and global warming.
List on How Wood Stoves Benefit the Environment:
- Renewable Resource
- Reduced Carbon Footprint
- Less Reliance on Fossil Fuels
- Supports Local Economies
- Waste Reduction
- Energy Independence
- Biodiversity
- Reduced Particulates
As the world grapples with these pressing environmental challenges, the search for cleaner, more sustainable heating solutions becomes paramount. Enter wood stoves, a time-honored method of heating, now reimagined with modern technology. As homeowners and environmentalists alike seek viable alternatives to fossil fuels, wood stoves are emerging as not just a nod to nostalgia but as a genuinely eco-friendly heating solution. The question then arises: How exactly do wood stoves benefit the environment, and are they a practical solution for the 21st-century household?
1. Renewable Resource
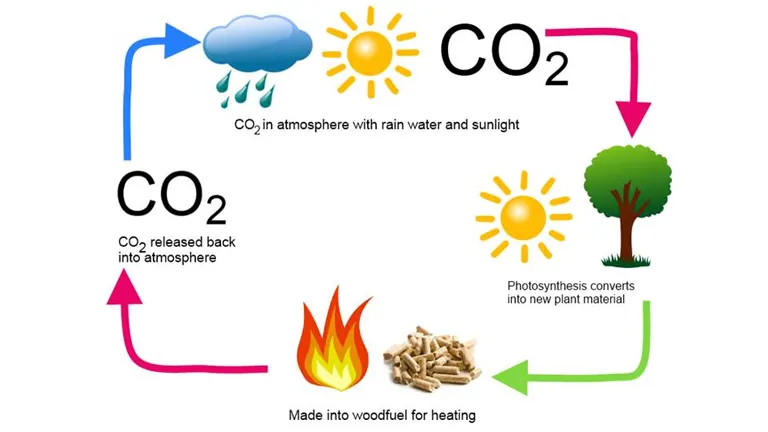
One of the primary environmental advantages of wood stoves lies in the nature of the fuel they use. Wood, particularly when it’s sourced from sustainably managed forests, stands out as a renewable resource. Unlike non-renewable fuels, which diminish over time and cannot be replaced within a human lifespan, wood is continuously replenished through the growth of new trees.
The carbon cycle of wood is a fascinating process that underscores its eco-friendliness. As trees grow, they actively absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, a major greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming. This absorbed carbon is stored within the tree’s structure, playing a vital role in its growth and development. When the wood from these trees is burned in stoves, the stored carbon is released back into the atmosphere as CO2. This cycle — from absorption during growth to release during combustion — creates a balanced, carbon-neutral loop. Essentially, the amount of CO2 emitted during burning is roughly equivalent to the CO2 the tree absorbed during its lifetime.https://googleads.g.doubleclick.net/pagead/ads?client=ca-pub-5935796446046681&output=html&h=280&adk=192126526&adf=2832010653&pi=t.aa~a.3093108475~i.21~rp.4&w=766&fwrn=4&fwrnh=100&lmt=1698333628&num_ads=1&rafmt=1&armr=3&sem=mc&pwprc=9138078273&ad_type=text_image&format=766×280&url=https%3A%2F%2Fforestry.com%2Freviews%2Feco-friendly-heating-how-wood-stoves-benefit-the-environment%2F&fwr=0&pra=3&rh=192&rw=766&rpe=1&resp_fmts=3&wgl=1&fa=27&uach=WyJXaW5kb3dzIiwiMTAuMC4wIiwieDg2IiwiIiwiMTE2LjAuNTg0NS4xOTAiLFtdLDAsbnVsbCwiNjQiLFtbIk5vdClBO0JyYW5kIiwiMjQuMC4wLjAiXSxbIkNocm9taXVtIiwiMTE2LjAuNTg0NS4xOTAiXV0sMF0.&dt=1698333632681&bpp=3&bdt=1878&idt=3&shv=r20231024&mjsv=m202310230101&ptt=9&saldr=aa&abxe=1&prev_fmts=0x0&nras=2&correlator=3844098734307&frm=20&pv=1&ga_vid=1920924023.1698333631&ga_sid=1698333631&ga_hid=635852995&ga_fc=1&u_tz=-600&u_his=1&u_h=768&u_w=1360&u_ah=728&u_aw=1360&u_cd=24&u_sd=1&dmc=8&adx=210&ady=1738&biw=1185&bih=480&scr_x=0&scr_y=0&eid=44759876%2C44759927%2C31079078%2C44805932%2C44806737%2C31078297%2C31079149%2C44806254&oid=2&pvsid=3780678367423776&tmod=114642110&uas=0&nvt=1&fc=1408&brdim=78%2C206%2C78%2C206%2C1360%2C0%2C1202%2C480%2C1202%2C480&vis=1&rsz=%7C%7Cs%7C&abl=NS&fu=128&bc=31&ifi=3&uci=a!3&btvi=1&fsb=1&xpc=fu9kZPlJZ5&p=https%3A//forestry.com&dtd=15
In stark contrast, fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas introduce an imbalance in the carbon equation. When burned, they release carbon that has been sequestered deep within the Earth for millions of years. This sudden influx of ancient carbon into the atmosphere is a significant driver of climate change. By relying on wood as a heating source, we can mitigate the environmental impact associated with fossil fuel consumption and support a more sustainable, carbon-neutral future.
2. Reduced Carbon Footprint

As environmental awareness has grown, so too has the technology behind wood stoves. Modern wood stoves represent a significant evolution from their predecessors, built with both efficiency and the environment in mind. When we speak of a reduced carbon footprint in the context of wood stoves, we’re referring to the total amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere over the stove’s lifetime, from manufacturing to everyday use.
One of the standout features of contemporary wood stoves is their combustion efficiency. Through advanced engineering and design, these stoves can extract more heat from a given amount of wood than traditional open fireplaces. This efficient combustion not only means that less wood is required to produce the same amount of heat but also results in fewer emissions per unit of heat produced.https://googleads.g.doubleclick.net/pagead/ads?client=ca-pub-5935796446046681&output=html&h=280&adk=192126526&adf=1351663300&pi=t.aa~a.3093108475~i.41~rp.4&w=766&fwrn=4&fwrnh=100&lmt=1698333628&num_ads=1&rafmt=1&armr=3&sem=mc&pwprc=9138078273&ad_type=text_image&format=766×280&url=https%3A%2F%2Fforestry.com%2Freviews%2Feco-friendly-heating-how-wood-stoves-benefit-the-environment%2F&fwr=0&pra=3&rh=192&rw=766&rpe=1&resp_fmts=3&wgl=1&fa=27&uach=WyJXaW5kb3dzIiwiMTAuMC4wIiwieDg2IiwiIiwiMTE2LjAuNTg0NS4xOTAiLFtdLDAsbnVsbCwiNjQiLFtbIk5vdClBO0JyYW5kIiwiMjQuMC4wLjAiXSxbIkNocm9taXVtIiwiMTE2LjAuNTg0NS4xOTAiXV0sMF0.&dt=1698333632689&bpp=3&bdt=1885&idt=3&shv=r20231024&mjsv=m202310230101&ptt=9&saldr=aa&abxe=1&cookie=ID%3D1cb59aeb6a5989df%3AT%3D1698333629%3ART%3D1698333629%3AS%3DALNI_MZqcEVzaBKemgO6Ij0solYw0lsEOw&gpic=UID%3D00000a369529d765%3AT%3D1698333629%3ART%3D1698333629%3AS%3DALNI_Ma6bYTv3cQ38STVYz8PjyPSlMenkw&prev_fmts=0x0%2C766x280%2C1185x480&nras=4&correlator=3844098734307&frm=20&pv=1&ga_vid=1920924023.1698333631&ga_sid=1698333631&ga_hid=635852995&ga_fc=1&u_tz=-600&u_his=1&u_h=768&u_w=1360&u_ah=728&u_aw=1360&u_cd=24&u_sd=1&dmc=8&adx=210&ady=2929&biw=1185&bih=480&scr_x=0&scr_y=1025&eid=44759876%2C44759927%2C31079078%2C44805932%2C44806737%2C31078297%2C31079149%2C44806254&oid=2&psts=AOrYGsm9LcqocYULP94zcOroJTbZVGIBkqLt6iWSpdgCaC_nsfNHSpguTW-qSTOxfggjFQZRK689x-shaYx9yCWBt91J5A&pvsid=3780678367423776&tmod=114642110&uas=3&nvt=1&fc=1408&brdim=78%2C206%2C78%2C206%2C1360%2C0%2C1202%2C480%2C1202%2C480&vis=1&rsz=%7C%7Cs%7C&abl=NS&fu=128&bc=31&ifi=4&uci=a!4&btvi=2&fsb=1&xpc=yn2knPJVfK&p=https%3A//forestry.com&dtd=74514
Furthermore, the latest wood stove models are subject to rigorous emission standards. Here are some of the key organizations and their roles in ensuring cleaner and more efficient wood-burning:
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, commonly referred to as the EPA, plays a pivotal role in the realm of wood heating. They set the standards for residential wood heaters across the United States, ensuring that these devices meet specific emission limits. One of their significant contributions is the certification process they’ve established, which aids consumers in identifying wood stoves that burn more cleanly and efficiently.
- European Environmental Agency (EEA): The European Environmental Agency, or EEA, is a crucial body in Europe’s push for a cleaner environment. They provide invaluable data and insights about the continent’s environmental status. Additionally, the EEA has been instrumental in the development and implementation of environmental regulations pertaining to wood-burning stoves, ensuring that they align with Europe’s broader sustainability goals.
- World Health Organization (WHO): Health and the environment often go hand in hand, and the World Health Organization, known globally as WHO, underscores this connection. They offer comprehensive guidelines on air quality, ensuring that people are aware of the standards that need to be met for public health. Moreover, WHO provides detailed information on the health impacts of various pollutants, including those emitted from burning wood, enlightening the public on potential risks and considerations.
- Blue Sky Alliance: The Blue Sky Alliance is an international organization with a focused mission: to reduce emissions originating from wood-burning stoves. Recognizing the global appeal and utility of wood stoves, especially in developing countries, the alliance tirelessly promotes cleaner technologies. Their initiatives ensure that as wood stoves become more prevalent, they do so without compromising the environment.
- The Alliance for Green Heat: Based in the U.S., The Alliance for Green Heat is a staunch advocate for wood and pellet heating. They champion these methods as not only viable but also as low-carbon and sustainable solutions for households. By promoting efficient wood heating, they aim to steer the conversation towards more environmentally friendly heating alternatives, pushing for a greener future.
By choosing a modern wood stove, homeowners are making a conscious decision to lower their carbon footprint. Not only do they benefit from efficient heating, but they also contribute to a cleaner environment by reducing the release of harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases.
3. Less Reliance on Fossil Fuels

As the global community grapples with the challenges of climate change, there’s a pressing need to transition away from non-renewable energy sources. Fossil fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas have been the primary drivers of our energy systems for decades, but their environmental and socio-economic costs are becoming increasingly evident.
By choosing wood stoves as a primary or supplementary heating source, households can significantly reduce their reliance on these fossil fuels. Here’s a closer look at the benefits of this shift:
- Environmental Impact: One of the most immediate advantages of using wood for heating is its environmental profile. Unlike fossil fuels, which release vast amounts of greenhouse gases when burned, wood’s carbon-neutral nature ensures that the CO2 emitted during combustion is balanced by the CO2 absorbed during the tree’s growth. This contrasts starkly with the one-way carbon release associated with burning fossil fuels.
- Economic Stability: Fossil fuel prices are notoriously volatile, influenced by a myriad of factors ranging from geopolitical tensions to extraction costs. Households that rely heavily on these fuels for heating can find their expenses fluctuating wildly from one season to the next. In contrast, wood, especially when sourced locally, tends to have more stable pricing, offering homeowners predictability in their heating costs.
- Energy Security: On a broader scale, a nation’s heavy dependence on imported fossil fuels can make it vulnerable to supply disruptions. Geopolitical issues, trade disputes, and other international events can jeopardize the steady flow of these fuels, leading to potential energy crises. By promoting wood-based heating, regions can move towards greater energy self-sufficiency, reducing their exposure to such external risks.
- Supporting Sustainable Practices: As the demand for wood as a heating source grows, there’s a concurrent push for sustainable forestry practices. This ensures that wood extraction is balanced by replanting efforts, creating a sustainable loop that benefits both the environment and the economy.
4. Supports Local Economies

In an era where globalization dominates economic discussions, the importance of supporting local businesses and economies often takes center stage, especially when it comes to sustainable practices. The decision to heat homes with wood has broader implications than merely environmental benefits; it’s also a significant economic driver for local communities.
- Direct Economic Impact: At its core, the purchase of firewood directly supports local loggers, transporters, and sellers. These are often small-scale operations or family-run businesses that rely on the local demand for wood to sustain their livelihoods. By choosing firewood as a primary heating source, homeowners directly infuse money into these local businesses, helping them grow and prosper.
- Job Creation: The wood heating industry, though perhaps not as vast as the fossil fuel sector, plays a crucial role in job creation at the local level. From forest management and logging to transportation and sales, multiple roles are interlinked in the firewood supply chain, offering employment opportunities for many in the community.
- Circulation of Money within the Community: When you spend money locally, it has a multiplier effect. Local businesses, benefiting from the sale of firewood, are more likely to reinvest their earnings within the community, whether it’s by purchasing local goods, availing local services, or employing residents. This continuous circulation of money strengthens the local economy, making it more resilient and vibrant.
- Reduced Economic Leakages: On the flip side, a heavy reliance on fossil fuels often means that a significant chunk of money spent on heating goes to large multinational corporations. These entities might have little to no direct connection to the local communities where their products are consumed. The money spent on fossil fuels often exits the local economy, leading to economic leakages and reduced local investment.
- Promotion of Sustainable Practices: By supporting the local wood heating industry, communities also indirectly promote sustainable forestry practices. As demand grows, there’s an incentive for loggers and forest managers to adopt sustainable logging methods, ensuring that forests remain a renewable resource for generations to come.
5. Waste Reduction

Waste reduction is a cornerstone of sustainable living. In our quest to minimize our environmental footprint, finding value in what’s typically discarded can lead to innovative solutions. Wood stoves, in this context, play a pivotal role in transforming potential wood waste into a resource, ensuring that nothing goes to waste.
- Utilizing Leftovers: In many woodworking processes, from lumber mills to carpentry workshops, there’s a significant amount of wood waste generated. These offcuts, shavings, and discarded pieces, rather than ending up in landfills or being burned in open spaces, can be effectively used as fuel for wood stoves, ensuring every bit of the resource is utilized.
- Benefiting from Natural Waste: Nature, too, produces its share of wood waste. Fallen branches after storms, dead trees, or those trimmed for safety or aesthetic reasons can all be repurposed. Instead of viewing these as waste, they can be seen as a valuable, renewable source of energy.
- Reducing Disposal Costs: For municipalities and communities, especially in areas where tree maintenance, landscaping, and removal are frequent activities, disposing of wood waste can be both a logistical challenge and a financial burden. By promoting the use of this waste wood for heating, these costs can be significantly reduced, and resources can be channeled to other pressing needs.
- Lowering Emissions from Open Burning: In many places, wood waste, especially from landscaping or storm clean-up, is often burned in open spaces. This method releases a significant amount of greenhouse gases and particulates. By using this wood in stoves, the combustion is more controlled and efficient, leading to fewer emissions and a cleaner burn.
- Promoting Circular Economy Principles: At its heart, using waste wood in stoves embodies the principles of a circular economy, where resources are used, reused, and recycled to the maximum extent possible, reducing the need for new resource extraction and minimizing waste.
6. Energy Independence

In an age where global events can quickly disrupt traditional energy supplies, achieving energy independence has become more crucial than ever. Wood stoves provide homeowners with an avenue to attain a level of self-sufficiency in their heating needs, ensuring warmth and comfort even in unpredictable situations.
- Decentralized Energy Source: One of the standout features of wood as a heating source is its decentralized nature. Unlike centralized heating systems that rely on extensive infrastructure and distribution networks, wood stoves operate at the individual or household level. This decentralization reduces vulnerabilities associated with large-scale system failures or disruptions.
- Shielding from Market Volatility: Global energy markets can be unpredictable, with prices for oil, gas, and electricity prone to sudden spikes due to geopolitical events, natural disasters, or supply-demand imbalances. With a wood stove, homeowners have the flexibility to source their wood locally, insulating them from global market fluctuations and ensuring more stable heating costs.
- Reliability During Power Outages: Wood stoves operate without the need for electricity, making them invaluable during power outages. While those relying on electric heating systems may find themselves without heat during a blackout, wood stove users can continue to enjoy a warm and cozy environment.
- Reduced Vulnerability to Supply Chain Disruptions: Recent events have highlighted the fragility of global supply chains. Disruptions in one part of the world can have cascading effects, impacting the availability and cost of goods and services elsewhere. By relying on locally sourced wood, homeowners can mitigate the risks associated with such disruptions, ensuring a consistent and reliable fuel supply.
- Supporting Local Resilience: On a broader scale, communities that embrace wood-based heating can bolster their overall resilience. In the face of external shocks, be it natural disasters or economic downturns, a community that has a degree of energy independence can recover and adapt more effectively.
7. Biodiversity

Biodiversity, the variety of life found in a particular habitat or ecosystem, is a crucial aspect of our planet’s health. It ensures ecosystem resilience, provides food and medicine, and plays a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate. Sustainably managed forests, which are a primary source of wood for eco-friendly stoves, play a pivotal role in maintaining and enhancing this biodiversity.
- Selective Logging: One of the key principles of sustainable forestry is selective logging. Instead of clear-cutting large areas, only certain trees are harvested, allowing the forest to regenerate naturally. This approach ensures that the forest’s structure and diversity remain largely intact, providing habitat for a wide range of species.
- Maintaining Natural Habitats: Sustainably managed forests prioritize the conservation of critical habitats. By setting aside areas that are rich in biodiversity or serve as habitats for endangered species, these forests ensure the survival of diverse plant and animal life.
- Corridor Conservation: Sustainable forestry practices also focus on maintaining green corridors, allowing wildlife to migrate and move freely. These corridors prevent habitat fragmentation, a significant threat to biodiversity, ensuring that isolated populations can interbreed and maintain genetic diversity.
- Soil and Water Protection: Proper forest management takes into account the health of the soil and water systems. By preventing excessive logging and ensuring ground cover, these forests prevent soil erosion, maintain water quality, and ensure the survival of aquatic ecosystems.
- Carbon Sequestration and Climate Regulation: Forests play a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate by absorbing carbon dioxide. Sustainably managed forests ensure that this carbon sequestration continues over the long term, providing a buffer against climate change, which is a significant threat to global biodiversity.
- Economic Incentives for Conservation: By creating a demand for sustainably sourced wood, eco-friendly stoves provide an economic incentive for forest managers to adopt and maintain sustainable practices. This market-driven approach can be a powerful tool for conservation, ensuring that forests are valued not just for the wood they produce but for the biodiversity they support.
8. Reduced Particulates

Air quality is a vital component of environmental and public health. Particulate matter, tiny particles suspended in the air, can have adverse health effects when inhaled, especially for individuals with respiratory conditions. Traditional methods of wood burning, such as open fires, can release a significant amount of these particulates. However, the landscape of wood combustion has evolved dramatically with the advent of modern wood stoves, designed with both efficiency and air quality in mind.
- Advanced Combustion Technology: Modern wood stoves incorporate advanced combustion technologies that optimize the burning process. This not only ensures that the wood is burned more completely, reducing waste but also minimizes the release of unburned particles and gases.
- Secondary Burn Systems: Many contemporary stoves feature secondary burn systems. These are designed to reignite and burn off gases and particulates that were not combusted in the initial burn. By ensuring a secondary combustion phase, these systems drastically reduce the number of particulates that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere.
- Air Wash Systems: Another innovation found in modern wood stoves is the air wash system. This system introduces a flow of air that helps keep the stove’s glass clean, but more importantly, it aids in the combustion of particulates, further reducing emissions.
- Emission Standards and Certifications: Regulatory bodies in many countries have established stringent emission standards for wood stoves. To be certified, these stoves must undergo rigorous testing to ensure they release minimal pollutants. This push for regulatory compliance has driven manufacturers to prioritize clean combustion in their designs.
- Environmental and Health Implications: By reducing particulate emissions, modern wood stoves contribute to better air quality, which has a direct impact on environmental and public health. Cleaner air means healthier forests, ecosystems, and communities. For urban and suburban areas where air quality can be a concern, these stoves offer a more responsible way to enjoy wood-based heating.
Conclusion
Wood stoves offer an eco-friendly alternative to conventional heating methods. However, it’s essential to operate them correctly and source wood sustainably. By choosing a modern, efficient wood stove and burning only dry, seasoned wood, homeowners can enjoy a cozy, warm atmosphere while contributing positively to the environment.
FAQs
- Are stoves good for the environment?
Stoves, particularly modern wood-burning stoves, can be eco-friendly when used correctly. They offer a renewable alternative to fossil fuels, and when sourced from sustainably managed forests, the wood used is part of a carbon-neutral cycle. Additionally, advancements in stove technology have made them more efficient, leading to reduced emissions compared to older models. - Can you get wood burners that are good for the environment?
Yes, many contemporary wood burners are designed with the environment in mind. They adhere to strict emission standards and are equipped with advanced combustion technologies that minimize the release of particulates and greenhouse gases. When fueled with sustainably sourced wood, these burners can be a green choice for home heating. - Why are Wood Burning stoves more efficient?
Modern wood-burning stoves are designed to maximize the combustion of wood, ensuring that more heat is extracted from each piece. They often feature secondary combustion systems that burn off excess gases and particulates, leading to cleaner emissions. This efficient combustion means less wood is required to produce the same amount of heat, reducing resource consumption. - How do you use a wood stove efficiently?
To use a wood stove efficiently:- Always burn dry, seasoned wood, as it combusts more completely than wet wood.
- Maintain a hot, bright fire rather than a slow, smoldering one to reduce creosote buildup and ensure complete combustion.
- Regularly clean and maintain your stove to ensure optimal airflow and combustion.
- Use the air vents to control the burn rate and maintain an efficient flame.
- Periodically inspect the stove and chimney for any blockages or buildups.
- What are the benefits of using sustainably sourced wood?
Sustainably sourced wood comes from forests that are managed with ecological balance in mind. Using this wood ensures that forests remain healthy and biodiversity is preserved. Moreover, these forests are often replanted, ensuring a continuous supply of wood without depleting natural resources. By choosing sustainably sourced wood, you’re supporting responsible forestry practices that prioritize both the environment and the economy.

David Murray
Forestry Author
I’m David Murry, a forestry equipment specialist with a focus on chainsaw operation. With over 13 years of experience, I’ve honed my skills in operating and maintaining a wide range of machinery, from chainsaws to log splitters. My passion for the outdoors and commitment to sustainable forestry drive my work, which emphasizes safety, efficiency, and staying updated with industry advancements. Additionally, I’m dedicated to sharing my expertise and promoting environmental awareness within the forestry community.


Recent Comments